
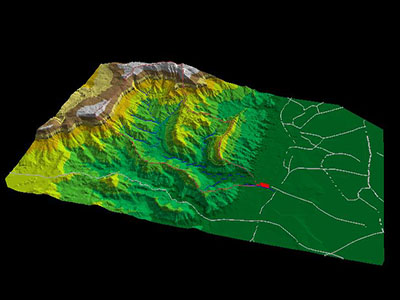
The factors that cause landslide disasters are topographical features, geological and soil characteristics, land use characteristics, and climate characteristics.
Landslides involve the movement of soil and various objects on the ground. The movement may occur on sloping terrain and may be influenced by water or moisture, providing lubrication. Landslides are characterized by the downward movement of soil from higher to lower elevations due to a loss of balance in the stability of the terrain. This results in the soil adjusting and flowing downward under the influence of gravity.
Landslides often occur during heavy rainfall in mountainous regions where the soil on the slopes becomes saturated. The lower layers of soil experience slow water infiltration, while the upper layers, already saturated, lose their cohesion. Combined with a slope in the terrain, this imbalance leads to the collapse or sliding of the soil mass downward.

The occurrence of landslides comprises four characteristics of movement:
1. Falls: This involves the detachment of a mass from a steep slope, causing it to fall as a large block or mass.
2. Topples: This refers to the forward tilting or rotation of a mass, causing it to fall or roll forward as a unit.
3. Slides: This is the movement of a mass along a surface, such as a curved or flat surface.
4. Flows: This involves the movement of a mass along an inclined slope, often facilitated by the presence of water.
The factors and components contributing to the occurrence of landslide disasters include:
1. Topographical Features: such as slope steepness, length of slopes, and the elevation of the area.
2. Geological and Soil Characteristics: Such as the composition of rocks and soil.
3. Land Use Characteristics: Including the impact of land use practices on soil cover.
4. Climatic Conditions: Such as precipitation.

We can classify strategies based on varying risk levels using geographical principles, landslide prevention, and mitigation. Analyzing landslide-prone areas requires consideration of fundamental factors, including the four mentioned factors. We use maps in analytical techniques to show landslide locations along with factors that contribute to landslides. The detailed examination and assessment of each factor's potential impact on landslides is made possible through this comparative analysis. When we identify areas resembling those where landslides have occurred in the past, it becomes clear which areas are at risk. GIS techniques are currently used to improve the analysis of landslide-prone areas. The integration helps identify areas prone to landslides with more clarity.
Once areas susceptible to landslides are identified at various levels, prevention and mitigation strategies can be tailored accordingly. We categorize these strategies based on different phases as follows.









Comments powered by CComment