Meteorology involves studying the ever-changing atmospheric conditions. In contrast, climatology focuses on studying long-term weather patterns.
General weather conditions refer to temperature, humidity, clouds, fog, wind, rain, and visibility. Understanding weather involves learning about the atmospheric conditions over a specific period, changing with days, times, and locations. For instance, the current weather in Bangkok today includes a high temperature of 40 degrees Celsius. On the other hand, understanding climate is about learning the recurring weather patterns over an extended period. Climate represents the average weather conditions for a particular region. For example, the climate in Bangkok has an average temperature of 27 degrees Celsius.
The atmosphere varies due to temperature, humidity, and air pressure. These components result from receiving radiation from the sun, and they all differ due to six key factors, namely:
1. Latitude: Affects the amount of solar radiation received from the sun due to the Earth's axis being tilted at 23 degrees from the vertical. As the Earth revolves around the sun, the inclination varies, with the northern and southern hemispheres alternating. Consequently, each region receives different amounts of solar radiation.
2. The difference between land and water: Land and water possess distinct characteristics that affect heat release and absorption.
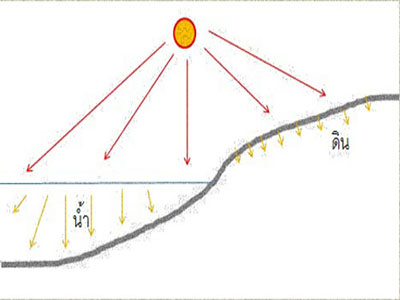
2.1 Water surfaces are transparent, allowing light to penetrate deeply. When exposed to sunlight, the heat spreads widely and deeply. Part of the heat is utilized for the evaporation of water, causing the water surface to heat up more slowly than land. In regions where heat disperses deeply, heat dissipation is consequently slower.
2.2 The land absorbs light, making it difficult for light to penetrate. When exposed to sunlight, heat disperses minimally, and the heat remains mainly at the surface of the soil. As a result, the land heats up faster than water and releases heat more rapidly than water surfaces.
3. Elevation above sea level in the region: The atmospheric layer immediately above the Earth's surface is the Troposphere. This layer experiences a temperature decrease with altitude at a rate of 6.4 degrees Celsius per 1 kilometer, which is the normal lapse rate. The temperature at higher elevations above sea level decreases.

4. Ocean currents are continuous flows of water along the coastlines, whether they originate from the poles towards the equator or from the tropics towards higher latitudes. These currents have an impact on the air temperature in the regions through which they flow.
5. The topographical characteristics affect the climate, such as mountain ranges acting as barriers to the movement of air, influencing the temperature and humidity on either side of the mountains.

6. Human activities influence the atmosphere, such as the use of ozone-depleting chemicals, the creation of industrial plants, and deforestation.