Improving map data in GIS with field data surveys using maps. We need consideration to determine the type of data feature.
Mapping is a representation of the characteristics of the Earth's surface, either globally or in specific regions, achieved through the process of scaling down and using symbols to represent various details present on the terrain. It is crucial to understand the features of a map, which include.
1. Transferring the characteristics of the Earth's surface to a flat plane.
2. Scaling down.
3. Symbols.
Consequently, it is essential to grasp the importance of recording data on the map throughout all three main components. Understanding minimization or scale is essential for accurately mapping the earth's surface onto a flat map using symbols. In this context, scale represents the ratio between map distances and actual distances on the ground, with the map distance set as 1 unit.
The map scale is 1:1,000, meaning that 1 unit on the map is equal to 1,000 units on the ground. For example:
If it measures 1.2 inches on the map, that's equal to 1.2 x 1,000 inches, or 1,200 inches, which is 100 feet.
If it measures 10 centimeters on the map, that's equal to 10 x 1,000 centimeters, or 10,000 centimeters, which is 1 kilometer.
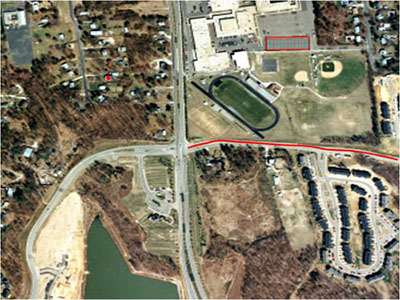
Improving map data in geographic information systems with field data surveys using maps. We need consideration to determine the type of data feature. The feature type in the country that will be imported into the mapping system, whether in hard copy or digital map format, can be categorized into three main types.
1. Positional Data (Point): Data without dimensions of width and length.
2. Route Data (Line): Data with both length and direction.
3. Area Data (Area/Polygon): Data with dimensions of width, length, and area.