Basic principles regarding field data collection with maps.
Once the feature type of the data has been determined, the field data collection process involves the following steps:
1. Accurately orienting the map's position according to the true geographical direction, as follows:
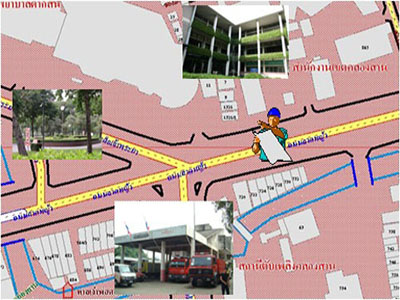
1.1 If the map has a compass symbol indicating the north, correctly align the map according to the true geographical direction.
1.2 With an incomplete map without a compass symbol, users should observe the actual geographical features and compare them with at least three points on the map. For example, if the district office is to the right, the fire station is to the left, and the hospital is in front of the map user, the user should assume their standing position on the map. If the district office is to the right, the fire station is to the left, and the hospital is in front, the user can then draw the north symbol on the map. Where the actual direction is unknown, users can observe the sun in the morning or evening to approximate east or west. The user can then draw an estimated north symbol on the map by standing with the right-hand facing east and the left-hand facing west, and the front will be considered north.
2. After that, the user can find three points on the map that correspond to the left, right, and front or back of their standing position, and compare them with the actual geographical features.
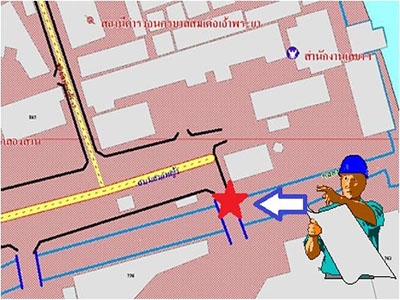
3. Recording data in the field onto a map. The process of recording data on a map, with knowledge of the scale or proportion of the map, can be easily accomplished. There are basic principles for data recording as follows:
3.1 Know the map scale:
- Calculate the distance in 1 map unit compared to the actual distance on the ground. For example, if the reference map used for data collection has a scale of 1:1,000, it means that 1 centimeter on the map is equivalent to 100 meters.
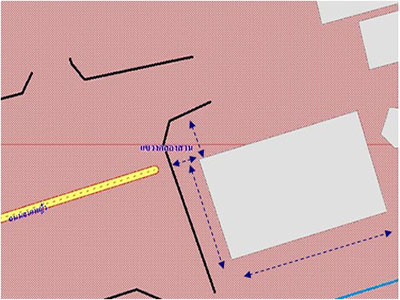
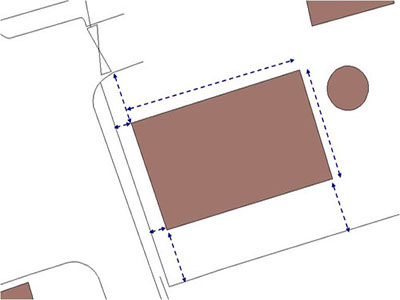
- Identify reference points and directions on the map.
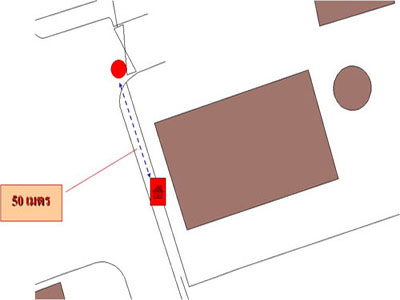
- Position the data, for example, when positioning a telephone booth about 50 meters away from the intersection, which may measure the distance by tape or the step between the points of interest and the points shown on the map.